MiniBox: A Two-Way Sandbox for x86 Native Code (ACT’14)¶
Link: https://www.usenix.org/conference/atc14/technical-sessions/presentation/li_yanlin
Problem to solve¶
Provides a two-way sandbox for x86 native code:
OS protection: prevent a benign OS from a misbehaving app (e.g., sandbox)
App protection: prevent an application from a malicious OS (e.g., SGX, enclave)
Risks in previously existing work:
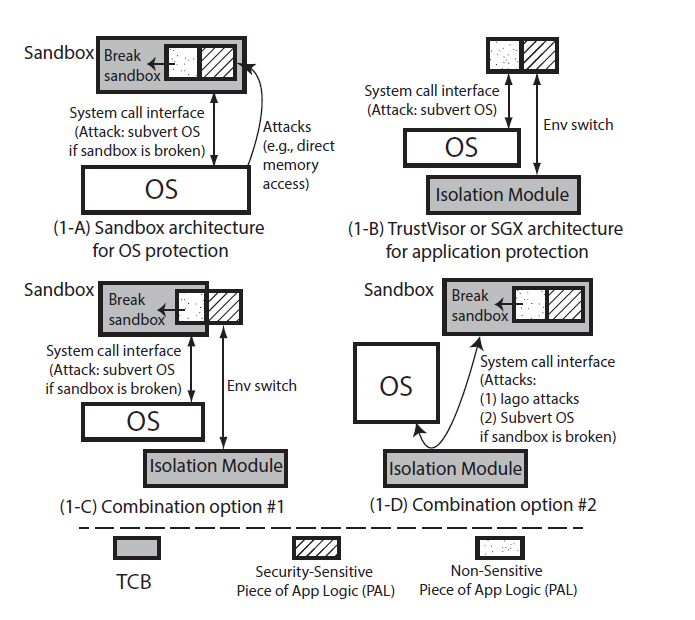
Iago attack: a malicious OS can subvert a protected process by returning a carefully chosen sequence of return values to sensitive system calls.
For example, a malicious OS returns a memory address that is in the application’s stack memory for an
mmapsystem callsensitive data (e.g., a return address) in the stack may subsequently be overwritten by the mapped data.
Methodology¶
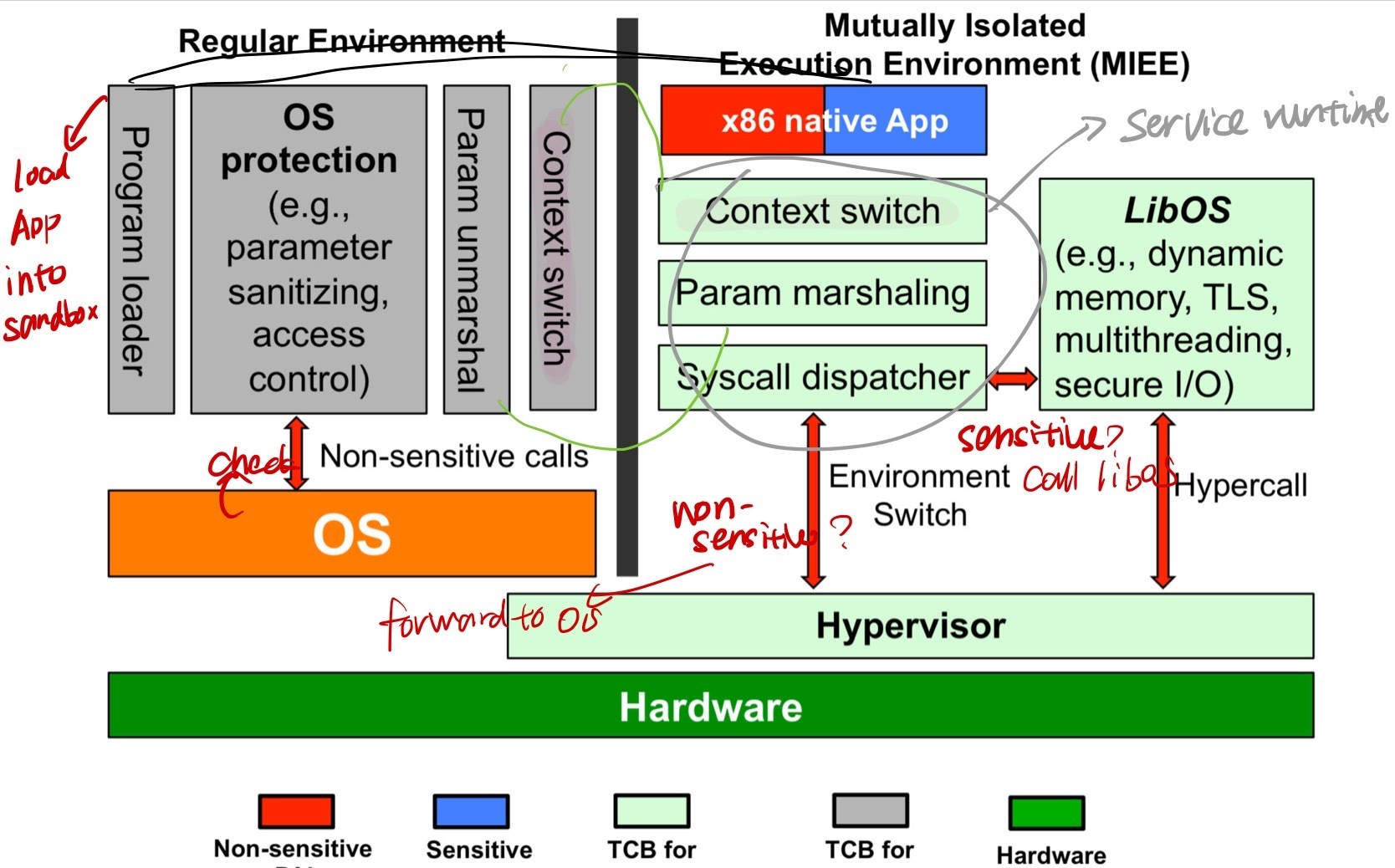
Service runtime module: support native app in MIEE
Context switch: stores and switches thread contexts between app and service
System call dispatcher: distinguishes between sensitive and non-sensitive system call, if non-sensitive, triggers an environment switch and forwards the call to the OS (via hypervisor), otherwise, forward to LibOS.
Param marshaling: encode the parameters (??? I think it should refer to the arguments in non-sensitive system calls)
OS protection modules
Program loader: sets up MIEE and load app into it.
Context switch: stores and restores the thread context between the regular environment and MIEE
parameter unmarshaling: decodes parameters
System call dispatcher: sanitizes the system call parameters, conducts access control to constrain the file access of the application, and forwards the non-sensitive system calls to corresponding handlers in the regular environment.
Remote Verifier¶
It directly adopts the mechanism in their previous work, TrustVisor, to enable a remote verifier to verify the integrity of the hypervisor, the service runtime, and the isolated application.
Dynamic Root of Trust for Measurement mechanism runs on commodity x86 processors
The chipset computes an integrity measurement (cryptographic hash) of the hypervisor, and extends the resulting hash into a Platform Configuration Register (PCR) in the Trusted Platform Module (TPM).
TrustVisor computes an integrity measurement for each registered PAL (Piece of Application Logic), and extends that measurement result into the PAL’\(\mu\)TPM instance. (\(\mu\)TPM: small TPM abstract for each PAL)
The TPM Quote from the hardware TPM
The \(\mu\)TPM Quote from the PAL’s \(\mu\)TPM instance
Multi-threading¶
If applying a 1:1 thread model like NaCl and using the OS to handle thread-related system calls, the OS controls the thread context of the application threads, which could break CFI of the application by changing the thread context. So it keeps all thread context in MIEE by duplicating all supported thread synchronization system call handlers.